The global shift to renewable energy is here, but sources like solar and wind come with a fundamental challenge: intermittency. The sun sets, and the wind calms down. This variability is a major hurdle for our electrical grids, which were built for the steady, predictable power of traditional power plants.
The solution is a transformative technology known as a Battery Energy Storage System (BESS).
So, what is a BESS? Think of it as a massive, rechargeable "power bank" for the grid. It's an advanced system that captures electrical energy when it's abundant and cheap, like from a solar farm at midday, stores it, and then releases that power exactly when and where it's needed most. A BESS doesn't generate new energy; it stores and dispatches previously generated energy, making it a uniquely flexible and vital tool for building a modern, clean, and resilient power grid.
For landowners, investors, and governments, understanding BESS is fundamental to capitalizing on one of the most significant technological shifts of our time. Let's dive in.
How a Battery Energy Storage System Works
The operation of a BESS follows a simple yet powerful three-stage cycle: charging, storing, and discharging.
First, the system charges by drawing electricity from a power source, like a solar farm or the wider electrical grid. During this process, electrical energy is converted into chemical energy and stored within the battery cells. In a typical lithium-ion battery, this involves moving lithium ions from one electrode to another.
Next, the captured energy is stored as electrochemical potential until it's needed. The amount of energy held is known as its "State of Charge" (SoC), which is simply a percentage indicating how full the battery is.
Finally, when the grid needs power, the system discharges. The process reverses, converting the stored chemical energy back into electrical energy and releasing it to power homes, businesses, or stabilize the grid.
The Critical Role of the Power Conversion System (PCS)
A crucial element enabling this cycle is the Power Conversion System (PCS), or inverter. Batteries store and release energy as Direct Current (DC), but our grids operate on Alternating Current (AC). The PCS acts as the essential, bi-directional bridge between the two. It converts DC power from the batteries into grid-compatible AC power during discharge, and it converts AC power from the grid into DC power to charge the batteries.
This two-way capability is what allows a BESS to not only supply power but also absorb it—a key feature for providing advanced grid stabilization services. While a traditional power plant takes time to ramp up, a BESS can respond in milliseconds. It operates at the speed of software, not mechanics, transforming it from a simple energy reservoir into a high-speed, digitally controlled grid management tool.
A BESS isn't just one giant battery. It's a sophisticated, integrated system of hardware and software working together.
The core of a BESS is its modular battery system. Individual cells are assembled into modules, which are arranged in racks. Multiple racks are then connected and housed in a secure, climate-controlled container or building. This modular design makes BESS highly scalable, from a single home to a massive utility-scale power station.
The Battery Management System (BMS) is the guardian of the battery's health and safety. It monitors key parameters like voltage, current, and temperature at the cellular level, preventing dangerous conditions like overcharging or overheating and balancing the charge across all cells to maximize the battery's lifespan.
If the BMS is the guardian, the Energy Management System (EMS) is the strategic "brain." This high-level software is what unlocks the revenue-generating potential of a BESS. By analyzing real-time grid prices, weather forecasts, and power demand, the EMS instructs the system when to charge, discharge, and what services to provide to the grid to maximize profitability.
Vital supporting systems include thermal management (like HVAC or liquid cooling) to keep the batteries at an optimal temperature and advanced safety systems, including fire detection and suppression, to ensure reliable and secure operation.
While the physical battery is the core component, the true driver of a project's return on investment is the sophistication of its Energy Management System. The hardware is becoming a commodity, but the intelligence of the software that controls it determines its profitability in complex, volatile energy markets.
A Comparative Look at BESS Battery Technologies
The choice of battery technology is a critical decision that impacts a project's performance, lifespan, and cost.
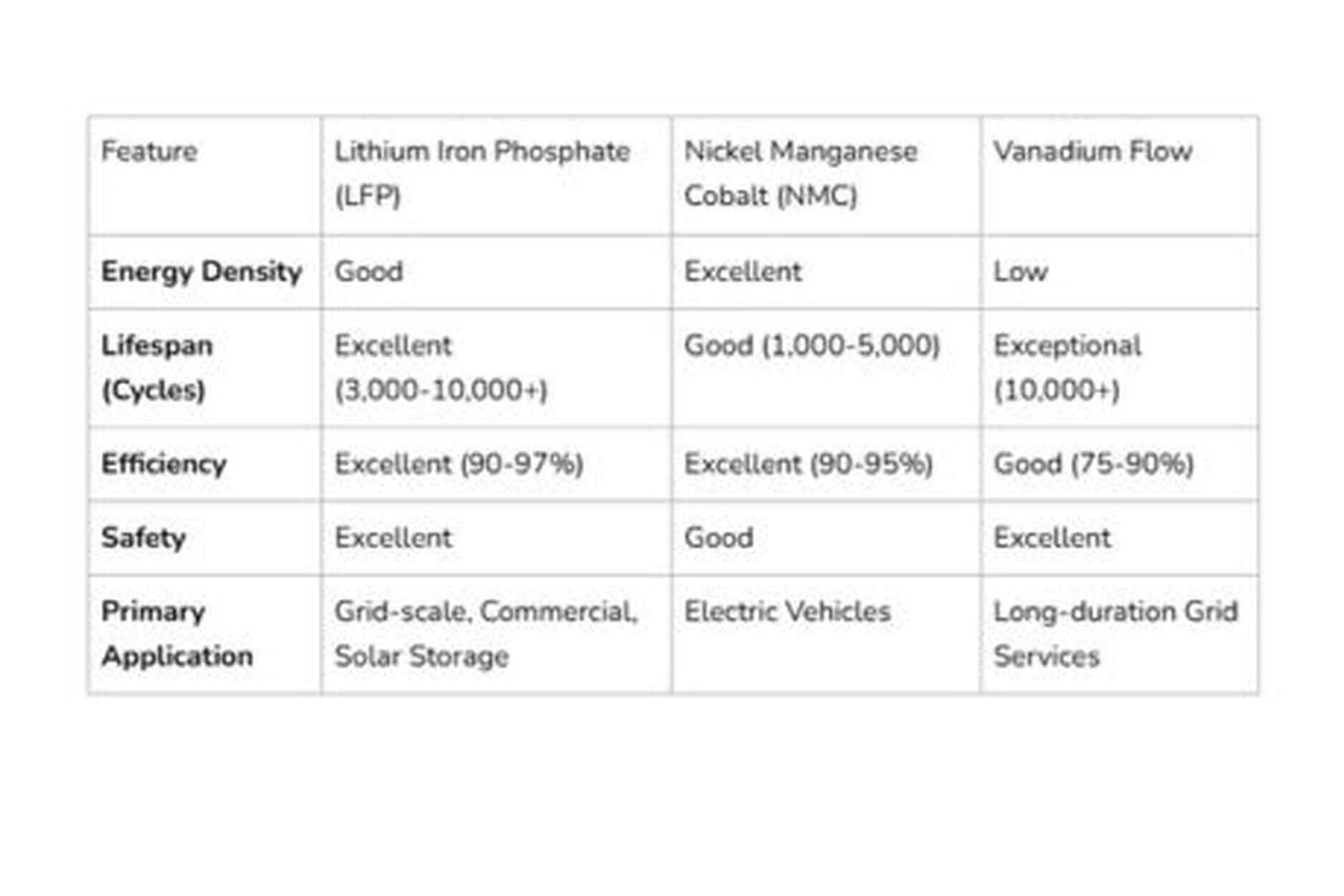
Lithium-Ion (Li-ion) is the dominant technology for grid-scale storage, thanks to its high energy density, excellent efficiency, and rapidly falling costs.
Lithium Iron Phosphate (LFP): This chemistry is quickly becoming the standard for stationary BESS due to its superior safety, exceptionally long cycle life, and lower cost, as it avoids using cobalt and nickel.
Nickel Manganese Cobalt (NMC): NMC offers higher energy density, making it popular for electric vehicles, but for grid applications, LFP is often preferred.
Flow Batteries are a promising contender for long-duration storage (4+ hours). They store energy in external tanks of liquid electrolyte, allowing energy capacity to be scaled independently of power. They offer an extremely long lifespan with minimal degradation.
Why BESS is Indispensable for the Energy Transition
Battery storage isn't just an accessory to clean energy; it's an essential component for building a decarbonized grid.
Unlocking Renewables: BESS solves the intermittency puzzle by making renewables a reliable, dispatchable power source. It stores excess solar or wind energy and delivers it when needed, preventing the wasteful practice of "curtailment."
Fortifying the Grid: BESS enhances grid stability and resilience. Its millisecond response is perfect for frequency regulation, and it can provide crucial backup power during outages caused by extreme weather.
Displacing Fossil Fuels: BESS is a cleaner, faster, and more cost-effective alternative to "peaker plants", inefficient and high-emitting gas generators that run only to meet peak demand.
Modernizing Infrastructure: Deploying BESS can defer or eliminate the need for costly upgrades to transmission lines by making the existing grid infrastructure more efficient.
A BESS is a versatile asset that creates compelling value for investors, landowners, and governments.
the BESS market is experiencing exponential growth, making it one of the most promising asset classes in the energy sector. Investors maximize returns through "revenue stacking"—generating multiple revenue streams like energy arbitrage (buying low, selling high), peak shaving for commercial customers, and providing ancillary services to the grid.
BESS projects offer a unique opportunity to generate stable, passive income. With a small physical footprint (a viable project can fit on less than a quarter of an acre), landowners can lease a small parcel for 20+ years, providing a reliable revenue stream with no upfront investment.
BESS is a critical tool for achieving climate goals, enhancing energy security, and driving economic growth. Incentives like the federal Investment Tax Credit (ITC) accelerate deployment, which in turn creates jobs and expands the local tax base.
The Perfect Synergy: Solar and Battery Storage
The combination of solar panels and a BESS, often called a solar-plus-storage system, creates a self-sufficient energy solution. The process is simple: solar panels generate electricity, which powers the facility's immediate needs. Any excess electricity is used to charge the battery. When the sun goes down, the facility draws clean, stored energy from the battery instead of expensive power from the grid.
This dramatically increases the self-consumption of "free" solar energy, maximizing the financial value and environmental impact of the solar asset.
Conclusion: The Future is Stored
A Battery Energy Storage System is a proven, transformative technology that is fundamental to the global energy transition. It's the key to unlocking a reliable, resilient, and fully decarbonized power grid by turning intermittent renewables into firm, dispatchable assets.
The opportunities are powerful and immediate. For investors, it's a high-growth asset class. For landowners, it's a stable, passive income stream. And for governments, it's an indispensable tool for achieving climate and economic goals. The energy storage revolution is here, and VIRIDI has the expertise to help you capitalize on the future of energy.
